Residual-based error corrector operator to enhance accuracy and reliability of neural operator surrogates of nonlinear variational boundary-value problems
Jun 21, 2023·
 ·
1 min read
·
1 min read
Prashant K. Jha
Abstract
This work focuses on developing methods for approximating the solution operators of a class of parametric partial differential equations via neural operators. Neural operators have several challenges, including the issue of generating appropriate training data, cost-accuracy trade-offs, and nontrivial hyperparameter tuning. The unpredictability of the accuracy of neural operators impacts their applications in downstream problems of inference, optimization, and control. A framework based on the linear variational problem that gives the correction to the prediction furnished by neural operators is considered based on earlier work in JCP 486 (2023) 112104. The operator, called Residual-based Error Corrector Operator or simply Corrector Operator, associated with the corrector problem is analyzed further. Numerical results involving a nonlinear reaction–diffusion model in two dimensions with PCANet-type neural operators show almost two orders of increase in the accuracy of approximations when neural operators are corrected using the correction scheme. Further, topology optimization involving a nonlinear reaction–diffusion model is considered to highlight the limitations of neural operators and the efficacy of the correction scheme. Optimizers with neural operator surrogates are seen to make significant errors (as high as 80 percent). However, the errors are much lower (below 7 percent) when neural operators are corrected.
Type
Publication
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering
 |
|---|
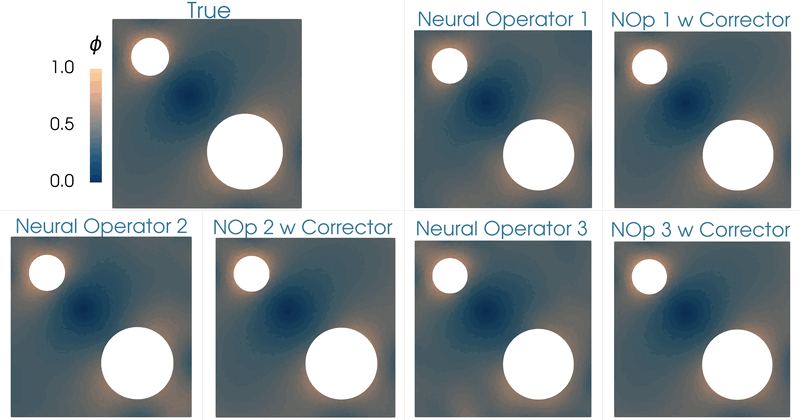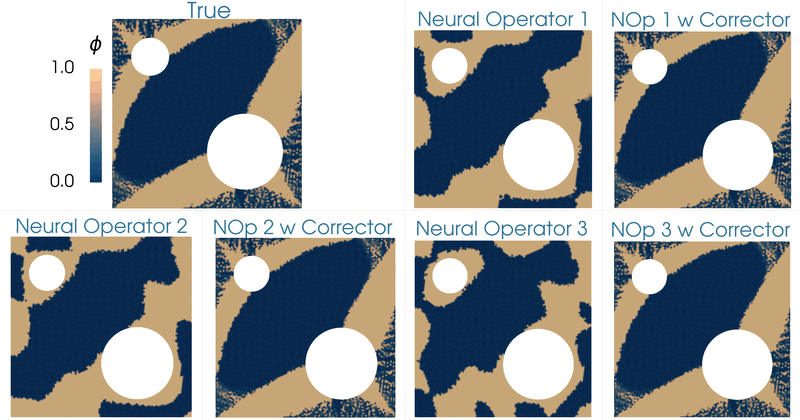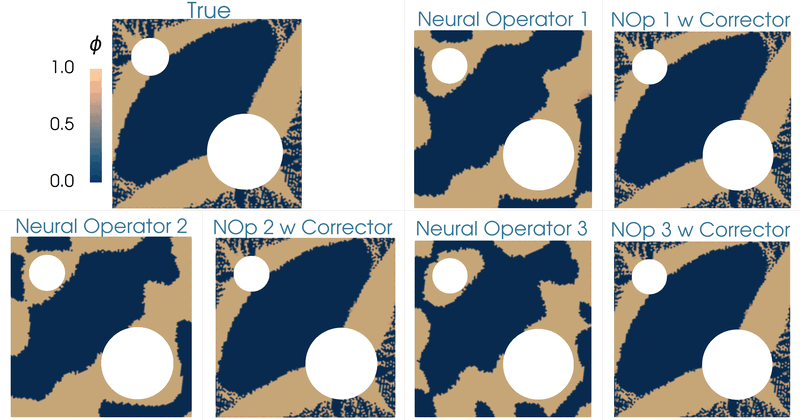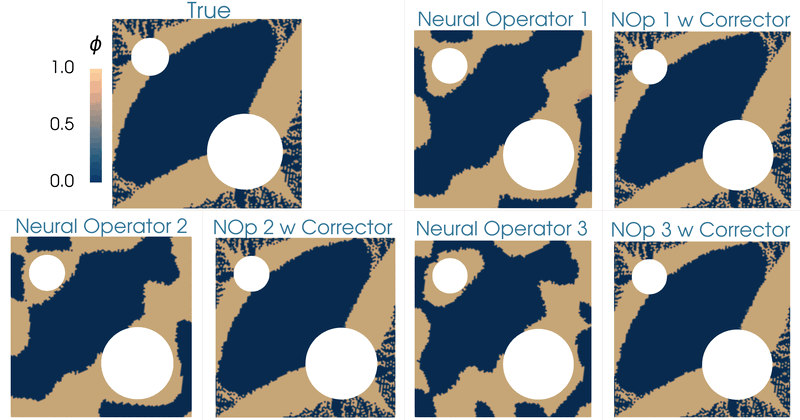
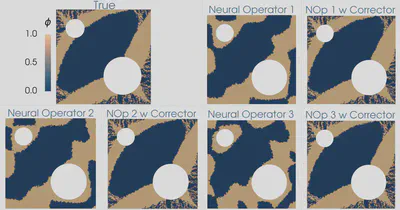
| Topology optimization of the diffusivity field in a nonlinear diffusion model. Neural operator and neural operator with corrector employed as a surrogate of the forward model. |
 |
|---|
| Comparing the optimizers of the topology optimization problem for different cases (1) true forward model, (2) neural operator surrogate of the forward model, and (3) neural operator with corrector. |
Neural Networks
Neural Operators
Variational Formulation
Partial Differential Equations
Topology Optimization
Computational Methods
Authors
Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering
Our group uses mechanics, applied mathematics, and computational science to understand and represent the complex behavior of materials, e.g., functional soft materials and granular materials.